Introduction to Version Control With Git And Github: Master the Basics
Version control is essential for developers. Git and GitHub are popular tools for this.
Understanding version control is crucial for managing code changes. Git helps track these changes efficiently. GitHub, a web-based platform, adds collaboration features. Together, they streamline development. Whether you work solo or in a team, mastering Git and GitHub boosts productivity.
This introduction will guide you through the basics. You’ll learn key concepts and how they work. Ready to dive in? Let’s explore Git and GitHub.

Credit: learning.nceas.ucsb.edu
What Is Version Control?
Version control is a system that tracks changes in files. It helps manage project history. Developers use it to collaborate efficiently. It allows multiple people to work on code simultaneously. This prevents overwriting each other’s changes. Version control keeps a record of modifications. This makes it easy to revert to previous states. It aids in identifying errors and exploring project evolution. It is crucial in software development.
Importance Of Version Control
Version control is vital for teamwork. It simplifies collaboration among developers. Everyone can contribute without conflict. It ensures code integrity. Mistakes can be undone easily. It helps in tracking progress. Developers can see who made changes and why. This boosts transparency. It allows safe experimentation. Trying new features without fear becomes possible.
Different Types Of Version Control Systems
There are various version control systems. Centralized systems store data in one location. Developers access a single repository. Examples include Subversion and CVS. Decentralized systems distribute repositories among users. Each user has a complete copy. Git and Mercurial are popular choices. They offer flexibility and independence. Version control systems vary in complexity. Choosing the right one depends on project needs.
Git Basics
Understanding Git basics is essential for anyone working with code. Git is a version control system. It tracks changes in files over time. This helps developers collaborate and manage projects efficiently.
History Of Git
Git was created by Linus Torvalds in 2005. He also developed the Linux kernel. Git emerged from a need for a better version control system. It was built to handle large projects with speed. Today, Git is widely used by developers worldwide.
Key Features Of Git
Git offers several powerful features. It’s a distributed version control system. This means every developer has a full copy of the project. Changes can be tracked and reversed easily. Git supports branching and merging. Developers can work on separate features without affecting the main code.
Git also ensures data integrity. It uses a cryptographic hash function to track changes. This prevents data corruption and loss. Moreover, Git is open-source. It’s free to use and supported by a large community.
Setting Up Git
Git simplifies tracking changes in code projects. It helps teams work together without losing updates. Linking Git with GitHub stores your work online safely. This setup is essential for coding collaborations.
Setting up Git is the first step to mastering version control, and it’s simpler than you might think. Whether you’re a newbie or an experienced coder, getting Git up and running on your machine is straightforward. With Git, you can manage your projects, track changes, and collaborate seamlessly with others. Let’s break down the process into easy-to-follow steps. ###Installing Git
The first thing you need to do is install Git on your computer. If you’re using a Windows machine, head over to the [Git official website](https://git-scm.com/) and download the installer. Follow the simple on-screen instructions to complete the setup. For macOS users, you can install Git using Homebrew. Open your Terminal and type: “`bash brew install git “` This command will download and install the latest version of Git. Linux users can install Git via their package manager. For instance, on Ubuntu, you can use: “`bash sudo apt-get install git “` Once the installation is complete, verify it by typing `git –version` in your terminal. You should see the version number of Git installed. ###Configuring Git
After installing Git, the next step is to configure it. This involves setting up your name and email address. These details will be associated with any commits you make and are essential for tracking changes. Open your terminal and enter: “`bash git config –global user.name “Your Name” git config –global user.email “[email protected]” “` Replace “Your Name” and “[email protected]” with your actual name and email. This information will be used in your commit messages to identify you as the author. You can also set your preferred text editor for Git. If you like using VS Code, you can set it with: “`bash git config –global core.editor “code –wait” “` This command ensures that VS Code will open up for you to write commit messages. Another useful configuration is setting up aliases for common Git commands. For instance, to make `git status` shorter, you can create an alias: “`bash git config –global alias.st status “` Now, you can simply type `git st` to check the status of your repository. Taking the time to configure Git to your liking can save you a lot of time and make your version control experience smoother. What configurations have you found most useful in your workflow?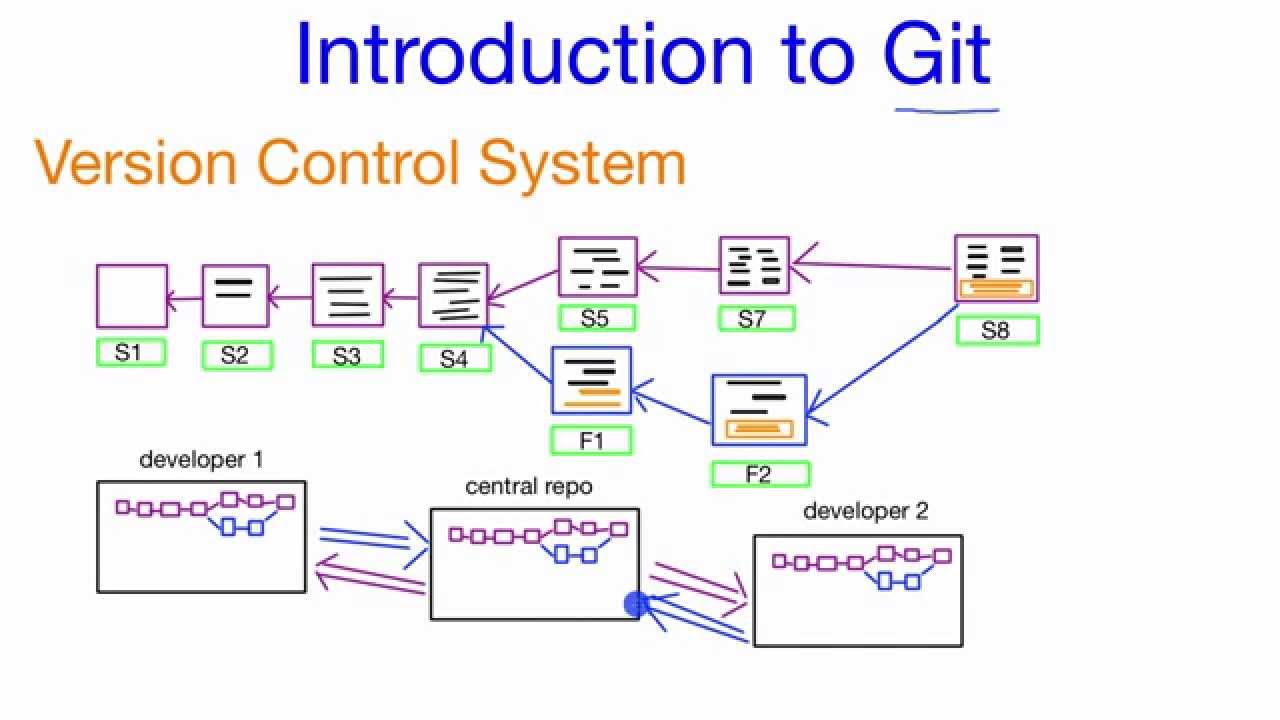
Credit: www.youtube.com
Basic Git Commands
Understanding basic Git commands is essential for effective version control. These commands help manage changes and track project history. They are simple yet powerful tools for developers.
Initializing A Repository
Starting a new Git project begins with initializing a repository. This process creates a hidden .git folder in the project directory. It stores all the necessary metadata for the project. To initialize, navigate to your project folder. Then, run the command git init in the terminal. Your folder is now a Git repository.
Committing Changes
Committing is saving changes to the repository. It records a snapshot of the project at a specific point. First, add the changes to the staging area using git add. You can add all changes with git add .. Next, commit the changes with git commit -m "Your commit message". This command saves the changes with a message describing them. It is important to write clear and concise commit messages.
Branching And Merging
Git and GitHub help manage code changes. Branching allows you to create separate paths for development. Merging combines these paths back into the main project.
Branching and merging are core features of Git and GitHub. They help manage changes in a collaborative software development environment. Understanding these concepts can improve project management. This section will dive into creating and merging branches.Creating Branches
Branches allow multiple people to work on a project simultaneously. Each branch represents a separate line of development. Creating a branch lets you work on a feature without affecting the main codebase. You can create a branch with a simple command. This command is `git branch branch-name`. Naming your branch helps in identifying its purpose. Use descriptive names like `feature-login` or `bugfix-header`. This practice keeps your branches organized.Merging Branches
Once a feature is complete, it’s time to merge branches. Merging integrates changes from one branch into another. It helps in bringing updates to the main project. To merge, switch to the branch you want to update. Use the command `git merge branch-name`. This command combines changes from the feature branch. Resolve any conflicts that arise during merging. Conflicts occur when two branches modify the same part of a file. Git will highlight these conflicts for you to address. After resolving, the merge completes, and changes become part of the main branch.Introduction To Github
GitHub is a popular platform for developers worldwide. It offers a host of features that make collaboration and code management easier. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, GitHub provides tools to enhance your workflow. Understanding GitHub is essential for anyone involved in software development.
What Is Github?
GitHub is a web-based platform for version control. It allows developers to store and manage code. GitHub is built on top of Git, a version control system. It provides a user-friendly interface for developers. With GitHub, teams can collaborate on projects seamlessly. It offers features to track changes and review code.
Key Features Of Github
One key feature is repositories. Repositories are storage spaces for your projects. They hold your code and project files. Another feature is branches. Branches help developers work on different code versions. They allow testing without affecting the main code.
GitHub also offers pull requests. Pull requests facilitate code reviews. They enable team members to discuss changes. Issues are another important feature. They help track bugs and tasks. GitHub Actions automate workflows. They streamline tasks like testing and deployment.
GitHub Pages is useful for hosting websites. It allows developers to publish their projects online. The platform supports integration with various tools. These integrations enhance productivity and collaboration.
Using Github With Git
GitHub is a web-based platform that works with Git. It helps developers store, manage, and share their code. GitHub makes collaboration easy. Developers can work together from different locations. Using GitHub with Git enhances productivity. It provides a seamless experience for version control.
Pushing To Github
Pushing to GitHub means sending your changes to the online repository. First, make sure your changes are committed locally. After committing, use the command git push origin main. This sends your updates to GitHub. It’s important to push regularly. This keeps your online repository up to date.
Remember, only committed changes are pushed. If you forget to commit, your changes stay local. Regular pushes help track progress. This is vital in collaborative projects. Everyone can see the latest code and updates.
Pulling From Github
Pulling from GitHub means downloading changes from the online repository. Use the command git pull origin main. This updates your local repository with the latest changes. Pulling is essential for teamwork. It ensures everyone works on the latest version.
Before starting new work, always pull first. This prevents conflicts and ensures smooth progress. Keep your local repository updated. It helps maintain code integrity. Pulling frequently is a good practice. It enhances collaboration and consistency.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Collaborating On Github
Explore the basics of version control with Git and GitHub for seamless collaboration. Manage code, track changes, and work effectively with others. GitHub serves as a popular platform, offering tools to streamline teamwork on coding projects.
Collaborating on GitHub is a game-changer for developers. It allows you to work with others seamlessly, regardless of where they are. Imagine synchronizing your work with teammates across the globe without missing a beat. Do you remember the frustration of merging changes manually? GitHub takes that pain away. It provides tools that make collaboration intuitive and efficient.Forking Repositories
Forking a repository is like making your personal copy of someone else’s project. You can experiment without affecting the original code. This is perfect for testing new features or fixing bugs. After forking, the repository appears in your account. You have complete freedom to modify it as you wish. This step is crucial before you start contributing to open-source projects. Ever thought of contributing to your favorite open-source project? Fork it and start exploring the codebase at your own pace. You can always push your changes back to the original project when ready.Creating Pull Requests
Pull requests are your way of saying, “Hey, I made some changes. Can you take a look?” They are crucial for contributing to projects on GitHub. Once you’ve forked a repository and made your changes, a pull request is your next step. Creating a pull request opens a discussion about your changes. It’s not just about code; it’s about communication. You get feedback, learn from it, and possibly improve your code. Consider a time when feedback made your work better. Pull requests offer that opportunity. Engage with the community, refine your work, and become part of something bigger.Are you ready to dive into GitHub collaboration? Start by forking a project that interests you. Experience the satisfaction of contributing to a thriving developer community.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Git, Github, And Version Control?
Git is a distributed version control system for tracking code changes. GitHub hosts Git repositories online, facilitating collaboration. Version control manages code changes, ensuring tracking, backup, and collaboration.
How To Use Git And Github For Beginners?
Install Git, then create a GitHub account. Use `git init` to start a repository. Add files with `git add`. Commit changes using `git commit`. Push to GitHub using `git push`. Clone repositories with `git clone`. Use `git pull` to update local files.
Practice frequently to enhance your skills.
What Are The Three Types Of Version Control?
The three types of version control are: 1. Local version control. 2. Centralized version control. 3. Distributed version control.
What Is The Difference Between Git And Github?
Git is a version control system for tracking code changes. GitHub is a web-based platform for hosting Git repositories.
Conclusion
Mastering Git and GitHub simplifies your coding projects. They help manage changes and track progress. Many developers rely on these tools daily. You can collaborate easily with others. Share your code and work together. Git and GitHub offer great benefits for teamwork.
Start small and practice regularly. Soon, you’ll find them intuitive. Explore tutorials and resources online. Build your skills step by step. Enhance your coding efficiency with Git and GitHub. Keep learning, keep improving, and enjoy coding!